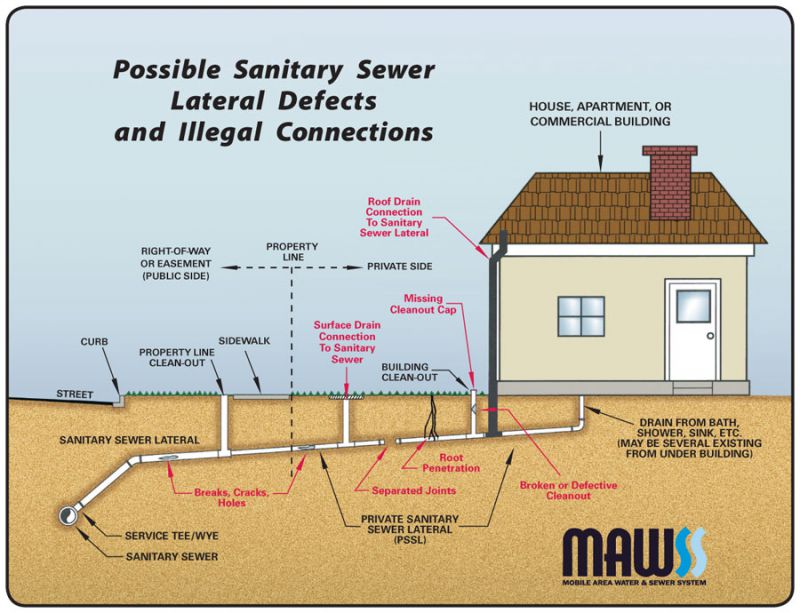
Mobile Area Water and Sewer System Help Prevent Sewer Problems
The sewer main in a large area is usually 3 to 5 feet in diameter, with the pipes from each house being about 6 to 12 inches in diameter on average. Sewer main infrastructure In every sewer.
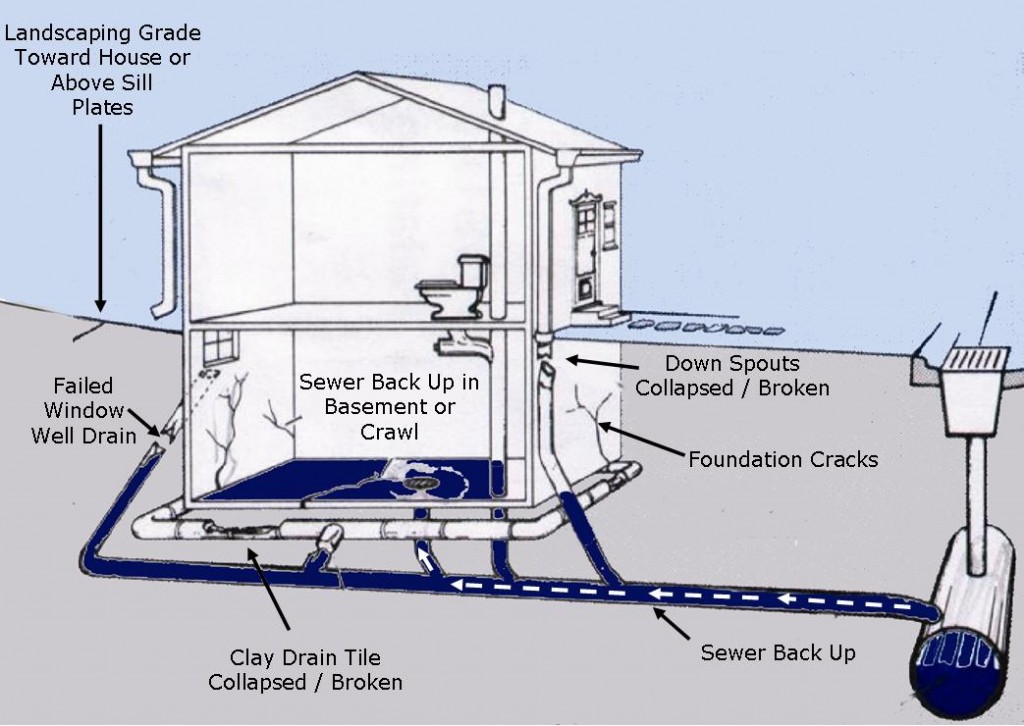
How to Troubleshoot Sewer Line Problems Pipe Spy
House Drainage System Diagram Image courtesy : Nations Home Inspection, Inc 1. Drain Lines Your house has several fixtures which uses water and discharges it out as wastewater. These are toilets, sinks, tubs, showers, washing machines, dishwashers etc.
How the Sewer Works DMMWRA, IA
A septic system drain field diagram is a visual representation of the layout and components of a septic system's drain field. Understanding this diagram can provide several benefits for homeowners: Proper Maintenance: Having knowledge of the drain field diagram allows homeowners to understand the location of various components, such as the.

Sewer Lines in Houston
A home sewer system is referred to in the plumbing trade as a house sewer. A house drain is a different system than a home sewer; a house sewer is located outside the house. A house drain refers to the main lateral drain line inside the building that is typically under the basement floor.

The Sewer System Basic Info & Pressure Tests North Tahoe Public
1. Install a pump chamber after the septic tank. The pump chamber or sometimes known as a pressure tank, or dosing tank contains the electric pump which is utilized to move the effluent from place to place, and eventually into the drain field for final disposal. [5] Set up the pump chamber as you would the septic tank.

Diagram House Sewer System Collections Get in The Trailer
Planning and installing a system that's quite, efficient, and leak free is something of an art Interested in the plumbing blueprint of your home? Check out this Roto-Rooter info-graphic that details plumbing blueprints of an average home.

Town Departments
A typical system consists of a waste pipe from the house, a large concrete, fiberglass, or plastic septic tank, and a leach field. The most common type of leach field consists of a series of perforated distribution pipes, each set in a gravel-filled absorption trench.
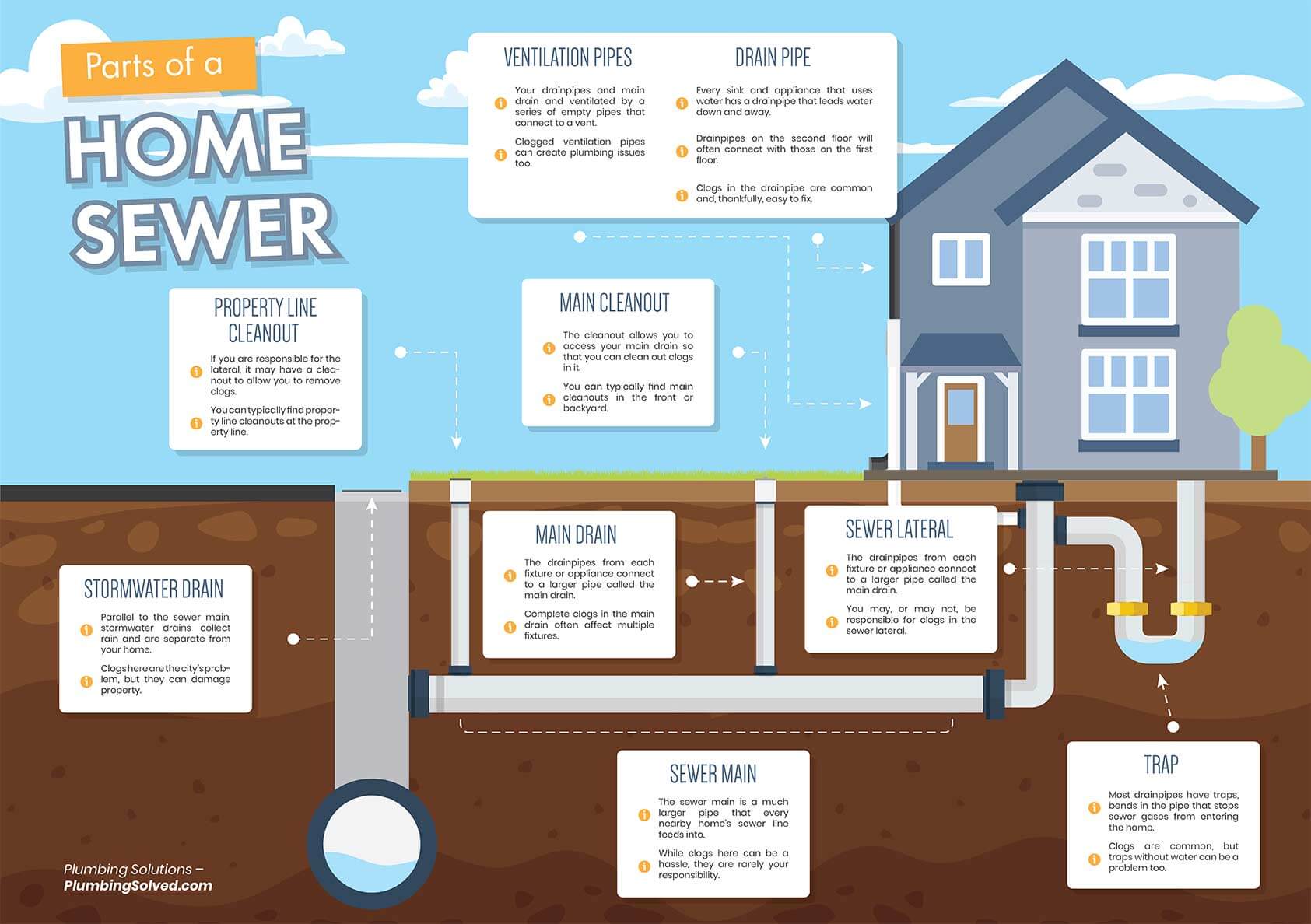
Parts of a Home Sewer System
A conventional decentralized wastewater treatment system consists of a septic tank and a trench or bed subsurface wastewater infiltration system, known as a drainfield. A conventional septic system is typically installed at a single-family home or small business. The gravel/stone drainfield is a design that has existed for decades.
Sewer Smarts and Plumbing Basics Superior, WI Official Website
how it works - diagram 1 Illustration. Inside the Septic Tank The middle liquid layer (effluent) then exits the tank and into the drain field. The drain-field is a shallow (covered) excavation ideally in unsaturated soil.
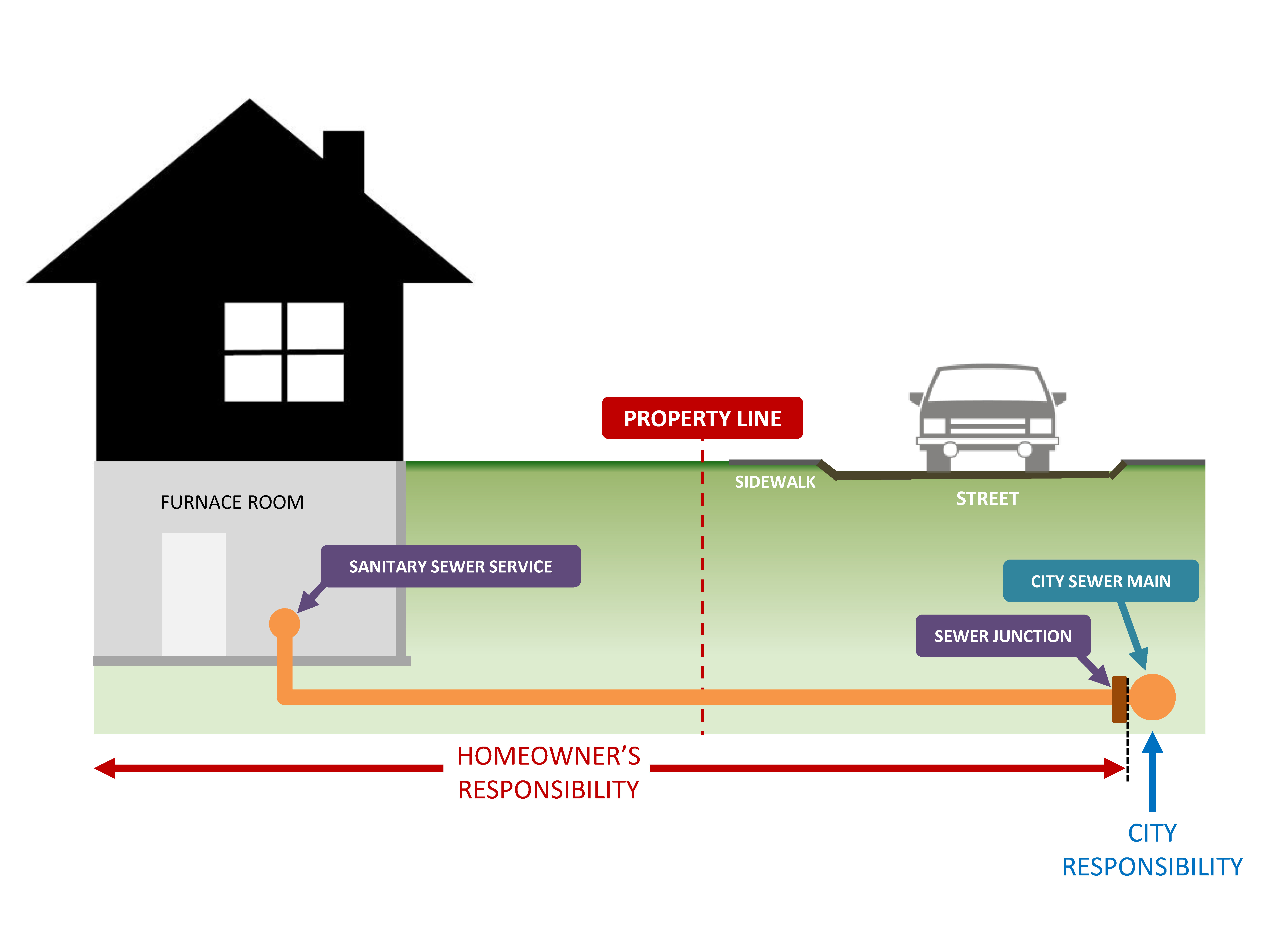
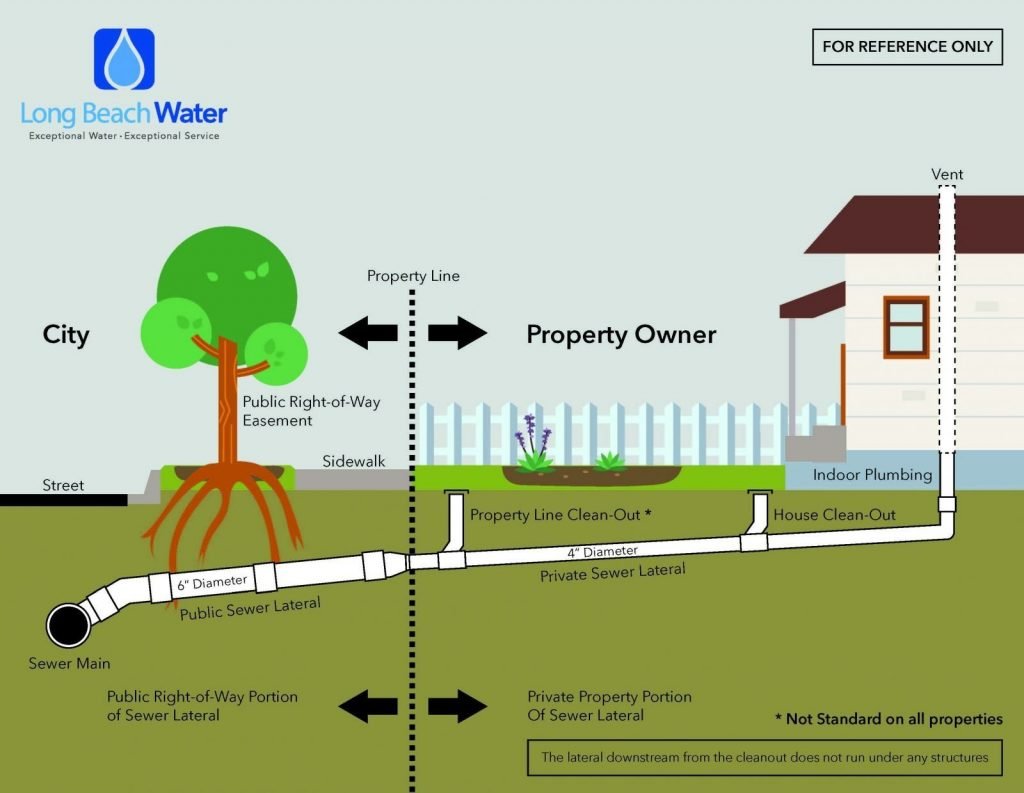
Property Owner Responsibilities
Combined Sewer System. Approximately 60% of New York City has a combined sewer system. This system uses a single pipe or a "combined sewer" to carry the flow of wastewater and stormwater to the local wastewater treatment plant. Managing stormwater in this system can pose challenges because during heavy rainstorms, combined sewers receive.

Combined Sewer System Diagram by Surfers against Sewage Flickr
After treatment, the system works by transferring ever-increasing quantities of water into increasingly smaller pipe networks. First, the regional pipes run many miles further than local pipes, and they can be anywhere between 8 to 144 inches wide depending on their location and purpose. These large pipes do most of the work of moving water.
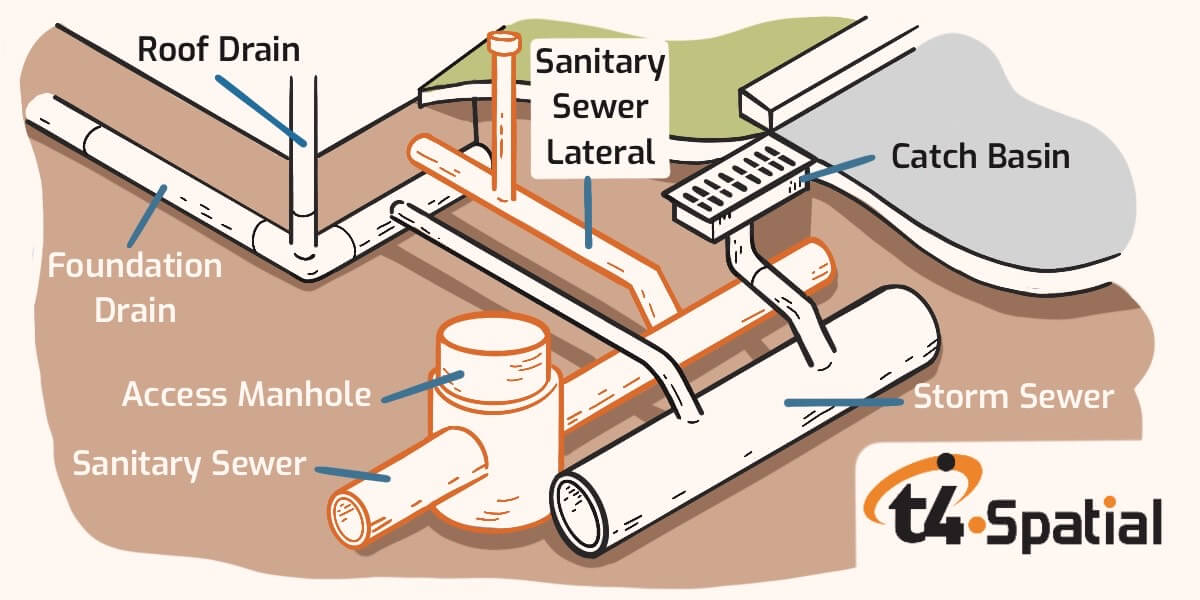
The Three Types of Sewer Systems and How They Work t4 Spatial
In this article, we will look at one of inner workings of sewer systems so that you can understand how they handle the billions of gallons of wastewater that the world produces every day! Contents Why Do We Need a Sewer System? Private Treatment: The Septic Tank Urban Wastewater Systems Measuring the Effectiveness of a Treatment Plant

MWRA How the Sewer System Works
2. Sanitary house sewer line A sanitary sewer, as its name implies, solely takes the flow of sanitary water. That is water used inside your home from toilets, sinks, showers, etc. All of this water gets treated by a public sewer treatment plant, or by a private septic system. 3. Storm sewer line
Sewer Scope Inspection Preparation Advice from the Experts
Septic System Sand and Gravel Filter Bed | iStock In most urban environments, when you flush the toilet, the waste is piped out to a sewage treatment plant. That plant treats and separates the waste into water that's clean enough to be discharged into a river and into solids called residual waste.

What Is The Difference Between a Septic System and A Sewer System
The whole home sewer system is made up of multiple parts coming together to form on complete system (See diagram below). When buying a home this can all get overwhelming. When broken down however, it is basically four parts: Internal plumbing: All of the plumbing drainage from inside the home i.e. sinks, toilets, tubs.

Design of Sewer System Civil Engineers PK
Septic systems efficiently treat and dispose of sewage and graywater, making them an integral part of many homes. However, not all septic systems are created equal. In fact, there are three primary types of septic systems, each with its own characteristics and suitability for different environments.